A chart to popularize chitin, chitosan and chitosan oligosaccharides
With the deepening development of glycobiology in recent years, chitin, chitosan and chitosan oligosaccharides have been discovered and put into research and development one after another, so what is the relevance and what is the difference between these three?
Chitin was discovered by French scholar Braqueño in 1811, and extracted from crustacean shells by Ogier in 1823 and named CHITIN, which translates as chitin. Appearance and properties: light beige to white. Chitin is the first practical application of the product, but also the first approved "functional food" in Japan. However, chitin is insoluble in water, alkali, general acids and organic solvents, only partially soluble in concentrated acids, and is partially decomposed by chitinase and lysozyme in the gastrointestinal tract of the human body, so its absorption rate is extremely low, and the dosage is large, and the reaction to take it is as high as 70% or more.
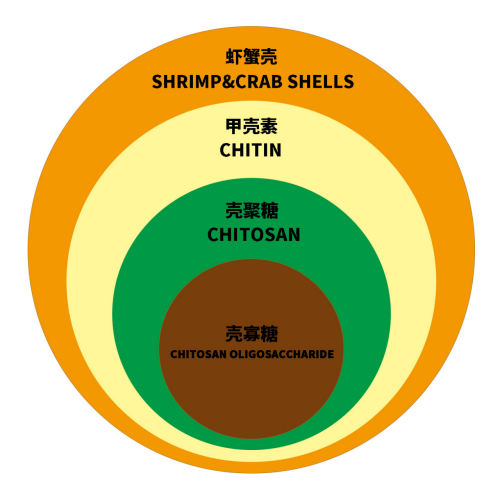
Chitin, also known as chitosan and chitin. It is extracted from chitin-containing substances such as shrimp shells and crab shells. White translucent solid. Insoluble in water, ethanol and ether. N-acetyl α-amino-D-glucosamine is a nitrogenous polysaccharide linked by β(1→4) glycosidic bond. Soluble in concentrated inorganic acid and anhydrous formic acid. Hydrolyzed in concentrated acid or concentrated base to form α-glucosamine. Chemical treatment of chitin to remove the acetyl group, then become chitosan.
Chitosan, also known as soluble chitin, chitosan, and chitosan amine, chemically known as polyglucosamine (1-4)-2-amino-B-D-glucose, is obtained by deacetylation of chitin, which is a kind of natural biopolymer. Generally speaking, chitosan can be called chitosan when more than 55% of N-acetyl group is removed. Chitosan is already soluble in dilute acids, which is a step forward from chitin. However, chitin and chitosan are both large molecules, with molecular weights ranging from several hundred thousand to several million, and both are insoluble in water. Chitin is deacetylated to obtain chitosan, and then after further degradation, it becomes chitosan oligosaccharide.
Chitosan oligosaccharide, also known as amino-oligosaccharide, chitosan oligosaccharide, oligochitosan, is a kind of oligosaccharide product with polymerization degree between 2-10, molecular weight ≤3500Da, good water solubility, great functionality, high biological activity and low molecular weight, which is obtained by degradation of chitosan by bio-enzymatic technology. It is fully soluble in water and has many unique functions, such as being easily absorbed and utilized by living organisms. Chitosan oligosaccharide is the only positively charged cationic alkaline amino-oligosaccharide in nature, which is animal cellulose and known as "the sixth life element". Therefore, chitosan oligosaccharide itself is a mixture of monosaccharides and decasaccharides, each of which has its own functionality.





Specific difference between chitosan oligosaccharide and chitosan:
1、Difference in molecular weight: Chitosan oligosaccharide is a brand new product obtained from chitosan processed by special biological enzyme technology, with molecular weight below 3000 Da; Chitosan is a product of partial deacetylation of chitin, with molecular weight of 500-1,000,000.
2、Difference in solubility: chitosan oligosaccharide has lower molecular weight and can be completely dissolved in water; chitosan can only be dissolved in dilute acid solution. The enhancement of water solubility is an important factor affecting some physiological activities of chitosan oligosaccharide, only dissolved in water, it is possible to be absorbed and utilized by living organisms, showing biological activities, so chitosan oligosaccharide is easier to be absorbed by the human body, animals and plants.
3、 Functional difference: Chitosan oligosaccharide with molecular weight below 2000 shows unique physiological activities and functions, improving macrophage function; inhibiting tumor cell growth and metastasis; lowering cholesterol and blood lipids; antibacterial, antimicrobial and significant moisture-retaining and wicking abilities, and so on. Chitosan oligosaccharide with molecular weight below 5000 has the ability to hinder the growth and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria, promote protein synthesis and activate plant cells, thus promoting rapid plant growth.
The many functions of chitosan oligosaccharide show that it is an alternative in the family of oligosaccharides. Chitosan oligosaccharide is the only alkaline, positively charged oligosaccharide found in the oligosaccharides, and this characteristic also determines that it is the only oligosaccharide that can be absorbed by intestines and enter into the blood circulation, and it is the basis for it to play many other biological functions when it reaches the whole body through the blood circulation. The prerequisite for intestinal absorption of chitosan oligosaccharide is that it is not digested by digestive enzymes. Chitosan is a polymer made of amino glucose linked by β-1,4-glycosidic bond, and the digestive enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract of human beings mainly act on α-1,4-glycosidic bond, so that chitosan oligosaccharide can maintain its structural integrity in the gastrointestinal tract.
In the field of agriculture, it can be used as crop immune inducer, plant vaccine, biostimulant; It can change the soil flora and promote the growth of beneficial microorganisms; Can induce disease resistance in plants, and produce immune and killing effects on many kinds of fungi, bacteria and viruses; It can be developed into biopesticides, growth regulators and fertilizers, etc.; the product is used in small quantities and has high economic benefits.
The above is for you to learn about the relationship between chitin, chitosan and chitosan oligosaccharides, I hope it can help you.



 Mobile: 86-13012553585 15610518510
Mobile: 86-13012553585 15610518510 Phone (Fax):86-53283197178
Phone (Fax):86-53283197178 E-mail: admin@bluealga.com
E-mail: admin@bluealga.com Add:No.918 Lingang 8 Road Huangdao District,Qingdao China 266400
Add:No.918 Lingang 8 Road Huangdao District,Qingdao China 266400

