Sargassum-Algae with Mysterious Power【2】
There are many species of Sargassum, and some of them often have variations in external morphology due to different regions, environments or ages, and even the morphology of the upper and lower parts of the same algal body can be very different from each other. Therefore, the different parts of some Sargassum algae can be easily named as several to more than ten species, which makes the phenomenon of different names for the same species and different species with the same name more common in the classification of Sargassum. Today, we introduce seven species of Sargassoaceae in detail.
Six of them are Sargassum C. Agardh and one is Hizikia0kamura. They are Copper algae, Sargassum, Watt's sargassum, Sea kibble, Split-leaf sargassum, Hemipterocarpus Chinese variant, and Sheepsheadia.
We continue today with the last four species
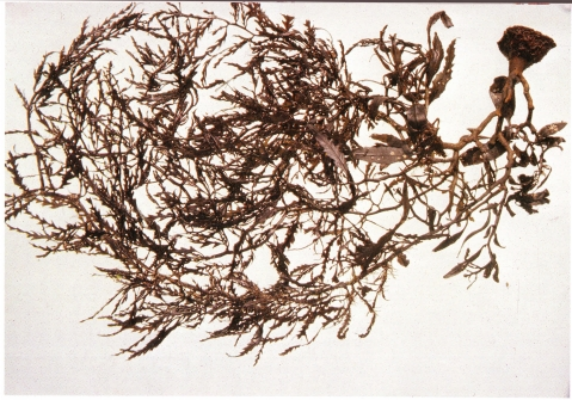
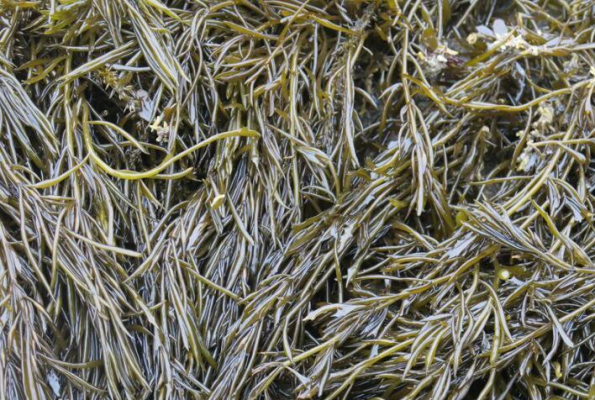
4. Sargassum muticum
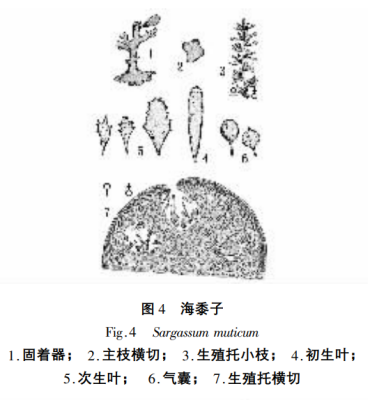

The body is brown, 400-600mm high, and the fixation apparatus is discoid or sub-garden cone-shaped. The main stem is about 10mm long, and the main branches are garden columnar, with obvious shallow grooves in the upper part, and obscure grooves in the lower part. Lateral branches alternate in all directions. Primary leaves are larger, obovate, 15-20mm long, rounded at the apex, short-stalked, without a midrib. Secondary leaves are shorter, about 10mm long, cuneate or asymmetrically semilobate, with toothed margins. The air sacs are globose, rounded at the apex or with a small protuberance, 2-3mm in diameter, and the stalks are about 2mm long (Fig. 4). Algae are monoecious and heterothallic. Reproductive stipes cylindrical, single or several clustered. The epidermal cells are finely rectangular in cross section of the receptacle. Spermatozoa small, inserted at the tips of lateral filaments. Oocysts round and small.
5. Sargassum siliquastrum
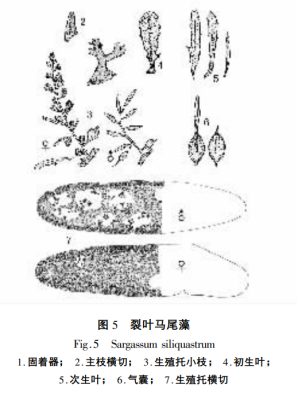

The body is brown, 300-600mm high, and the fixation apparatus is conical. The main stem is short, less than 10mm. 2-3 main branches, three-angled, slightly twisted, the lower leaves of the main branches strongly reflexed. Primary leaves obovate, midrib conspicuous, disappearing near leaf tip. Secondary leaves lanceolate, margin sparsely dentate, occasionally with a deep cleft near the midrib. Air sacs ellipsoidal, 9 mm in long diameter, 6 mm in short diameter, air sacs with small protuberances at the top or lanceolate corolla (Fig. 5). Reproductive receptacle leaf-shaped and flattened, female receptacle broad at the top and narrow at the bottom, one side of which is truncated and flat in the form of a grate; male receptacle slightly longer, fusiform and humorous compressed. In cross-section of the receptacle, the epidermal cells are finely oblong, the spermathecae are small, inserted on both sides of the base of the lateral filaments, and the oocysts are ellipsoid.
6. Sargassum hemiphyllum var. chinense
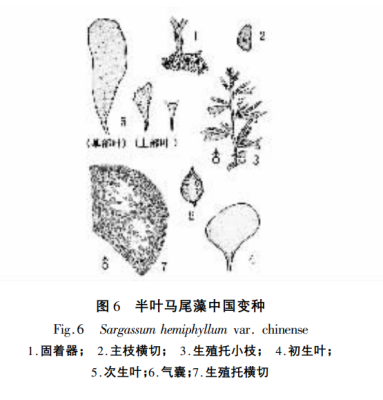

Body brown, 500-800mm high, up to 2m or more. Fixation apparatus pseudo-root-like compound forked branches. The main stem is 5-15 mm long, and the main branches are 2-3, smooth and unarmed, the lower part of which is flattened and rounded, and the upper part of which is tapered into a semi-cylindrical shape. Lateral branches alternate, in plane with main branches. Leaves without midrib. Primary leaves obovate or cuneate, slightly asymmetric, margin without teeth. Secondary leaves distinctly asymmetric, upper margin flat, arcuate-curved; lower margin rounded, toothed. Aerial sac globose, 5-6 mm in diameter, apex rounded or with a small protuberance, stipe short (Fig. 6). Algae dioecious. Reproductive receptacle terete, single or several concolorous, apex slightly pointed. In cross-section view of the receptacle, the epidermal cells are oblong, mostly singly inserted at the base of the lateral filaments.
Characteristics of the genus Ampelopsis Fixation apparatus pseudoradical. Main stem erect, terete. Branches cylindrical or subterete, secondary branches growing from the leaf axils of primary branches, relatively short. Algal leaves fleshy, plump, most of the primary algal leaves compressed, ovoid, but soon falling off, most of the secondary algal leaves clavate, obtuse or pointed at the tip, margins entire or shallowly serrate, their tips often inflated, transformed into aerial sacs, aerial sacs fusiform, ovoid, dioecious. The reproductive receptacle grows from the axils of the leaves, and is comparatively simple, oblong or cylindrical.
7. Hizikia fusiforme
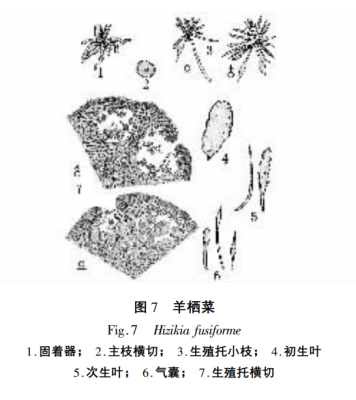

Yellowish brown, black after drying. Body height 200-400mm, up to 2m or more. Fixed apparatus pseudo-root-like branching. The main stem is extremely short, about 2-4mm. the main branches are smooth and terete, without longitudinal grooves. Primary leaves appear mostly at a young age, obovate, fleshy, entire, without a midrib. Secondary leaves rounded-clavate or lanceolate, dentate. Aerial sacs formed by the apical or central part of the rod-shaped leaves expanded and hollow, rounded or pointed at the apex (Fig. 7). Algae dioecious. Reproductive receptacle terete, several clustered from leaf axils of lateral branches of main branch. Female receptacle diameter 1.5mm male receptacle diameter 1mm, male and female receptacle length similar about 8mm. reproductive receptacle cross-section view, epidermal cells rectangular, middle of the cell on both sides of the concave. Spermathecae several clustered at the tip of lateral filaments, oocysts oval.



 Mobile: 86-13012553585 15610518510
Mobile: 86-13012553585 15610518510 Phone (Fax):86-53283197178
Phone (Fax):86-53283197178 E-mail: admin@bluealga.com
E-mail: admin@bluealga.com Add:No.918 Lingang 8 Road Huangdao District,Qingdao China 266400
Add:No.918 Lingang 8 Road Huangdao District,Qingdao China 266400

